Redis 调用
本章介绍如何在插件中调用 Redis、本地开发环境搭建、以及开发基于令牌桶限流插件。
1 Redis 调用
Higress 插件的 Go SDK 中 redis_wrapper.go 封装 Redis 调用, 部分核心代码如下:
// Redis 回调函数type RedisResponseCallback func(response resp.Value)
// Redis 调用接口type RedisClient interface { // 初始化接口 Init(username, password string, timeout int64) error // with this function, you can call redis as if you are using redis-cli } // 命令接口 Command(cmds []interface{}, callback RedisResponseCallback) error // Lua脚本接口 Eval(script string, numkeys int, keys, args []interface{}, callback RedisResponseCallback) error
// 以下是 Redis 各种命令接口 // Key Del(key string, callback RedisResponseCallback) error Exists(key string, callback RedisResponseCallback) error Expire(key string, ttl int, callback RedisResponseCallback) error Persist(key string, callback RedisResponseCallback) error ...}
// RedisClusterClient, Redis 调用接口具体实现type RedisClusterClient[C Cluster] struct { cluster C}
func RedisInit(cluster Cluster, username, password string, timeout uint32) error { return proxywasm.RedisInit(cluster.ClusterName(), username, password, timeout)}// 真正调用 Redis 的函数func RedisCall(cluster Cluster, respQuery []byte, callback RedisResponseCallback) error { requestID := uuid.New().String() _, err := proxywasm.DispatchRedisCall( cluster.ClusterName(), respQuery, func(status int, responseSize int) { response, err := proxywasm.GetRedisCallResponse(0, responseSize) var responseValue resp.Value // 获取 Redis 回调结果 responseValue ... if callback != nil { // 调用回调函数 callback(responseValue) } }) ... return err}所有调用 Redis 的接口,最终通过 RedisCall 调用 Redis, 同时回调 RedisResponseCallback 回调函数。
2 令牌桶限流
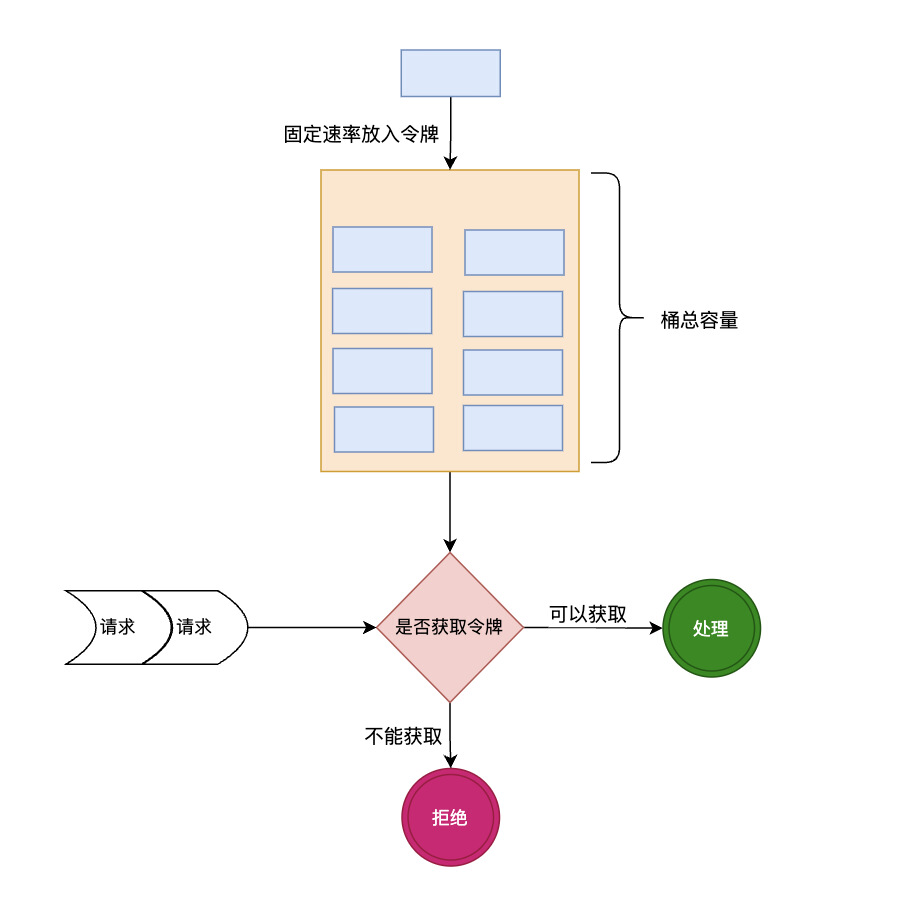
常见的限流算法有固定窗口限流算法、滑动窗口限流算法、漏桶限流算法、令牌桶限流算法等。这里主要介绍令牌桶限流算法。 令牌桶算法原理:
- 令牌以固定的频率被添加到令牌桶中。
- 如果令牌数量满了,超过令牌桶容量的限制,那就丢弃。
- 系统在接受到一个用户请求时,都会先去令牌桶要一个令牌。如果拿到令牌,那么就处理这个请求的业务逻辑。
- 如果拿不到令牌,就直接拒绝这个请求。
令牌桶算法允许一定量的突发请求,因为桶可以存储一定数量的令牌,从而在短期内处理更多的请求。具体原理见下图:
关于 QPS 限流算法和令牌桶算法两种限流算法优缺点,可以参考:限流算法选择。
3 本地开发环境搭建
3.1 初始化工程目录
- 新建一个工程目录文件 cluster-bucket-limit。
mkdir cluster-bucket-limit- 在所建目录下执行以下命令,初始化 Go 工程。
go mod init cluster-bucket-limit更详细信息参考第十四章 Wasm 插件介绍和开发自定义插件。
3.2 Makefile、Dockerfile、docker-compose.yaml、envoy.yaml 文件
- Makefile、Dockerfile
Makefile、Dockerfile 文件参考第十四章 Wasm 插件介绍和开发自定义插件。
- docker-compose.yaml
version: '3.9'services: envoy: image: higress-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/higress/gateway:v1.4.1 entrypoint: /usr/local/bin/envoy # 注意这里对wasm开启了debug级别日志,正式部署时则默认info级别 command: -c /etc/envoy/envoy.yaml --log-level info --log-path /etc/envoy/envoy.log --component-log-level wasm:debug depends_on: - echo-server networks: - wasmtest ports: - "10000:10000" - "9901:9901" volumes: - ./envoy.yaml:/etc/envoy/envoy.yaml - ./build/plugin.wasm:/etc/envoy/plugin.wasm - ./envoy.log:/etc/envoy/envoy.log echo-server: image: higress-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/higress/echo-server:1.3.0 networks: - wasmtest ports: - "3000:3000" redis: image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/2456868764/redis:latest environment: - ALLOW_EMPTY_PASSWORD=yes networks: wasmtest: ipv4_address: 172.20.0.100 ports: - "6379:6379"networks: wasmtest: ipam: config: - subnet: 172.20.0.0/24- envoy.yaml 文件
envoy.yaml 配置文件如下:
admin: address: socket_address: protocol: TCP address: 0.0.0.0 port_value: 9901static_resources: listeners: - name: listener_0 address: socket_address: protocol: TCP address: 0.0.0.0 port_value: 10000 filter_chains: - filters: - name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager typed_config: "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.network.http_connection_manager.v3.HttpConnectionManager scheme_header_transformation: scheme_to_overwrite: https stat_prefix: ingress_http route_config: name: local_route virtual_hosts: - name: local_service domains: ["*"] routes: - match: prefix: "/" route: cluster: echo-server http_filters: - name: wasmdemo typed_config: "@type": type.googleapis.com/udpa.type.v1.TypedStruct type_url: type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.wasm.v3.Wasm value: config: name: wasmdemo vm_config: runtime: envoy.wasm.runtime.v8 code: local: filename: /etc/envoy/plugin.wasm configuration: "@type": "type.googleapis.com/google.protobuf.StringValue" value: |- { "keys": [ "authorization" ], "in_header": true, "limits": [ { "name": "credential1", "consumer": "Bearer credential1", "rate": 2, "capacity": 4 }, { "name": "all", "consumer": "*", "rate": 1, "capacity": 2 } ], "rejected_code": 429, "rejected_msg": "Too Many Requests", "show_limit_quota_header": true, "redis":{ "service_name": "redis.static", "service_port": 6379, "timeout": 2000 } } - name: envoy.filters.http.router typed_config: "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.router.v3.Router clusters: - name: echo-server connect_timeout: 30s type: LOGICAL_DNS # Comment out the following line to test on v6 networks dns_lookup_family: V4_ONLY lb_policy: ROUND_ROBIN load_assignment: cluster_name: echo-server endpoints: - lb_endpoints: - endpoint: address: socket_address: address: echo-server port_value: 3000 - name: outbound|6379||redis.static connect_timeout: 30s type: STATIC load_assignment: cluster_name: outbound|6379||redis.static endpoints: - lb_endpoints: - endpoint: address: socket_address: address: 172.20.0.100 port_value: 6379envoy.yaml 配置文件增加了 outbound|6379||redis.static 集群,用于连接 Redis 服务。Redis 连接目前不支持 DNS 域名配置,只支持 IP 地址配置。
因此这里 Redis 的 IP 地址是 172.20.0.100。
3 令牌桶限流插件开发
3.1 插件配置和配置解析
插件配置和配置解析部分核心代码如下:
// LimitConfig 定义了限流插件的配置结构。type LimitConfig struct { Keys []string `yaml:"keys"` // 定义了用于提取限流信息的HTTP请求头字段名称。 InQuery bool `yaml:"in_query,omitempty"` // 标识是否从查询参数中获取限流信息。 InHeader bool `yaml:"in_header,omitempty"` // 标识是否从请求头中获取限流信息。 Limits []LimitItem `yaml:"limits"` // 包含具体的限流规则项。 RejectedCode uint32 `yaml:"rejected_code"` // 请求超过阈值被拒绝时返回的 HTTP 状态码。 RejectedMsg string `yaml:"rejected_msg"` // 请求超过阈值被拒绝时返回的响应体。 ShowLimitQuotaHeader bool `yaml:"show_limit_quota_header"` // 标识是否在响应头中显示限流配额信息。 RedisInfo RedisInfo `yaml:"redis"` // 定义了与 Redis 交互所需的信息。 RedisClient wrapper.RedisClient // Redis客户端,用于执行Redis命令。}
// LimitItem 定义了具体的限流项,包括限流名称、消费者标识、请求速率和容量。type LimitItem struct { Name string `yaml:"name"` // 限流项的名称。 Consumer string `yaml:"consumer"` // 限流项关联的消费者标识,用于匹配特定的请求。 Rate int `yaml:"rate"` // 每秒放入桶内的令牌数量。 Capacity int `yaml:"capacity"` // 限流桶的最大容量。}
// RedisInfo 定义了连接Redis所需的详细信息。type RedisInfo struct { ServiceName string `required:"true" yaml:"service_name" json:"service_name"` // Redis 服务名或地址。 ServicePort int `yaml:"service_port" json:"service_port"` // Redis 服务端口。 Username string `yaml:"username" json:"username"` // 连接 Redis 的用户名,如果需要。 Password string `yaml:"password" json:"password"` // 连接 Redis 的密码,如果需要。 Timeout int `yaml:"timeout" json:"timeout"` // 连接 Redis 的超时时间(毫秒)。}
// LimitContext 定义了限流上下文,存储了限流相关的信息。type LimitContext struct { Allowed int // 表示当前请求是否被允许。 Count int // 限流桶当前的计数。 Remaining int // 限流桶剩余的容量。 Reset int // 限流桶重置时间(秒)。}
// 解析配置,这里忽略插件配置解析的细节。主要显示 Redis 部分解析配置。func parseConfig(json gjson.Result, config *LimitConfig, log wrapper.Log) error { // keys names := json.Get("keys") ... // in_query and in_header in_query := json.Get("in_query") in_header := json.Get("in_header") ... // parse limit limits := json.Get("limits") ... config.ShowLimitQuotaHeader = json.Get("show_limit_quota_header").Bool()
// parse redis redisConfig := json.Get("redis") if !redisConfig.Exists() { return errors.New("missing redis in config") } serviceName := redisConfig.Get("service_name").String() if serviceName == "" { return errors.New("redis service name must not be empty") } servicePort := int(redisConfig.Get("service_port").Int()) if servicePort == 0 { if strings.HasSuffix(serviceName, ".static") { // use default logic port which is 80 for static service servicePort = 80 } else { servicePort = 6379 } } username := redisConfig.Get("username").String() password := redisConfig.Get("password").String() timeout := int(redisConfig.Get("timeout").Int()) if timeout == 0 { timeout = 1000 } config.RedisInfo.ServiceName = serviceName config.RedisInfo.ServicePort = servicePort config.RedisInfo.Username = username config.RedisInfo.Password = password config.RedisInfo.Timeout = timeout config.RedisClient = wrapper.NewRedisClusterClient(wrapper.FQDNCluster{ FQDN: serviceName, Port: int64(servicePort), }) log.Debugf("parseConfig()+%+v", config) return config.RedisClient.Init(username, password, int64(timeout))}这里忽略插件配置解析的细节,主要显示 Redis 解析配置。可以看出这里需要调用 wrapper.NewRedisClusterClient 方法初始化 RedisClient 和 RedisClient Init 方法初始化 Redis 连接。
3.2 插件限流 Lua 脚本
令牌桶限流的 Lua 脚本如下:
local tokens_key = KEYS[1]local timestamp_key = KEYS[2]--redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "tokens_key " .. tokens_key)
local rate = tonumber(ARGV[1])local capacity = tonumber(ARGV[2])local now = tonumber(ARGV[3])local requested = tonumber(ARGV[4])local unit = tonumber(ARGV[5])
local fill_time = capacity/ratelocal ttl = math.floor(fill_time*2*unit)
--redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "rate " .. ARGV[1])--redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "capacity " .. ARGV[2])--redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "now " .. ARGV[3])--redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "requested " .. ARGV[4])--redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "filltime " .. fill_time)--redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "ttl " .. ttl)
local last_tokens = tonumber(redis.call("get", tokens_key))if last_tokens == nil then last_tokens = capacityend--redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "last_tokens " .. last_tokens)
local last_refreshed = tonumber(redis.call("get", timestamp_key))if last_refreshed == nil then last_refreshed = 0end--redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "last_refreshed " .. last_refreshed)
local delta = math.max(0, (now-last_refreshed)/unit)local filled_tokens = math.min(capacity, last_tokens + math.floor(delta*rate))local allowed = filled_tokens >= requestedlocal new_tokens = filled_tokenslocal allowed_num = 0if allowed then new_tokens = filled_tokens - requested allowed_num = 1end
--redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "delta " .. delta)--redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "filled_tokens " .. filled_tokens)--redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "allowed_num " .. allowed_num)--redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "new_tokens " .. new_tokens)
if ttl > 0 then redis.call("setex", tokens_key, ttl, new_tokens) redis.call("setex", timestamp_key, ttl, now)end
return { allowed_num, new_tokens, capacity, ttl}Lua 脚本是在 Redis 中执行的,用于实现令牌桶限流算法。下面是对脚本参数和原理的分析:
- 参数解释:
- KEYS[1] 和 KEYS[2]:这两个参数是通过 Redis 调用传递的键(keys),通常用于存储令牌桶的当前令牌数(tokens_key)和最后刷新时间(timestamp_key)。
- ARGV[1] 到 ARGV[5]:这些参数是通过 Redis 调用传递的参数,用于配置限流策略。
- rate:单位时间内生成的令牌数量。
- capacity:令牌桶的容量,即最多可以容纳的令牌数。
- now:当前时间,通常以时间戳表示,以秒单位。
- requested:当前请求需要的令牌数。
- unit:令牌生成的时间单位,1 表示秒,60 表示分钟,3600 表示小时。
- 脚本原理:
- 初始化变量:根据传入的参数初始化令牌桶的填充时间和 TTL(生存时间)。
- 获取当前状态:从 Redis 中获取当前的令牌数(last_tokens)和最后刷新时间(last_refreshed)。如果不存在,则初始化为令牌桶的容量。
- 计算令牌填充:
- delta:自上次刷新以来经过的单位时间。
- filled_tokens:根据 delta 和 rate 计算应该填充的令牌数,但不能超过桶的容量。
- 判断是否允许请求:
- allowed:如果当前令牌数加上填充的令牌数大于等于请求的令牌数,则允许请求。
- 更新令牌数:
- 如果请求被允许,从当前令牌数中减去请求的令牌数,更新 new_tokens。
- 设置新的状态:
- 如果 TTL 大于 0,则更新 Redis 中的令牌数和时间戳,设置新的 TTL。
- 返回结果:
- 返回一个包含限流结果的数组,包括是否允许请求、新的令牌数、桶容量和 TTL。
3.3 插件限流具体实现
限流主要实现在插件 onHttpRequestHeaders 方法中,部分核心代码如下:
// onHttpRequestHeaders 函数在处理 HTTP 请求头时被调用,用于执行限流逻辑。func onHttpRequestHeaders(ctx wrapper.HttpContext, config LimitConfig, log wrapper.Log) types.Action { log.Debugf("onHttpRequestHeaders()") // 初始化 tokens 切片,用于存储从请求头或查询参数中提取的 tokens 信息 var tokens []string
// 如果配置指定从请求头中获取 tokens 信息 if config.InHeader { // 遍历配置中定义的所有键(key),尝试从请求头中获取每个键的值 for _, key := range config.Keys { // 使用 proxywasm 库的 GetHttpRequestHeader 函数获取请求头中的值 value, err := proxywasm.GetHttpRequestHeader(key) // 如果没有错误且值不为空,则将值添加到 tokens 切片中 if err == nil && value != "" { tokens = append(tokens, value) } } } else if config.InQuery { // 如果配置指定从查询参数中获取 tokens 信息 // 获取 ":path" 请求头以获取请求 URL requestUrl, _ := proxywasm.GetHttpRequestHeader(":path") // 解析 URL 并获取查询参数 url, _ := url.Parse(requestUrl) queryValues := url.Query()
// 遍历配置中定义的所有键 for _, key := range config.Keys { // 从查询参数中获取每个键的值 values, ok := queryValues[key] // 如果查询参数存在且有值,则将值添加到 tokens 切片中 if ok && len(values) > 0 { tokens = append(tokens, values...) } } }
// 如果从请求中提取了多于一个的 tokens,返回错误处理 if len(tokens) > 1 { return deniedMultiKeyAuthData() } else if len(tokens) <= 0 { // 如果没有提取到 tokens,返回错误处理 return deniedNoKeyAuthData() }
// 提取第一个 token 作为主要的令牌信息 limitKey := strings.Split(tokens[0], ",")[0] log.Debugf("limitKey:%s", limitKey)
// 根据提取的 limitKey 查找对应的限流项 limitItem := findLimitItem(config, limitKey) log.Debugf("limitItem:%+v", limitItem)
// 如果没有找到对应的限流项,继续处理请求 if limitItem.Consumer == "" { return types.ActionContinue }
// 构建 Redis 脚本需要的键,用于操作令牌桶 tokenKey := fmt.Sprintf(ClusterRateLimitFormat, limitKey, "token") expireKey := fmt.Sprintf(ClusterRateLimitFormat, limitKey, "expire")
// 获取当前时间,用于计算令牌桶的填充状态 now := time.Now() // 将当前时间转换为 Unix 时间戳(秒) unixTimestamp := now.UnixNano() milliseconds := unixTimestamp / 1e6 seconds := milliseconds / 1000
// 构建调用 Redis 脚本所需的参数 keys := []interface{}{tokenKey, expireKey} args := []interface{}{limitItem.Rate, limitItem.Capacity, seconds, 1, 1}
// 调用 Redis 脚本执行限流逻辑 err := config.RedisClient.Eval(BucketTokenScript, 2, keys, args, func(response resp.Value) { log.Debugf("RedisClient.Eval(),keys:%+v,args:%+v", keys, args) // 检查脚本返回的结果是否包含 4 个元素 resultArray := response.Array() if len(resultArray) != 4 { log.Errorf("redis response parse error, response: %v", response) proxywasm.ResumeHttpRequest() return } // 根据脚本返回的结果创建 LimitContext 对象 context := LimitContext{ Allowed: resultArray[0].Integer(), Remaining: resultArray[1].Integer(), Count: resultArray[2].Integer(), Reset: resultArray[3].Integer(), } log.Debugf("context:%+v", context) // 如果请求未被允许(Allowed <= 0),触发限流逻辑 if context.Allowed <= 0 { log.Debugf("request rejected") rejected(config, context) return } else { // 将限流上下文存储在 HttpContext 中,供后续处理使用 ctx.SetContext(LimitContextKey, context) } // 恢复 HTTP 请求处理 proxywasm.ResumeHttpRequest() }) // 如果调用 Redis 脚本时出现错误,记录错误并继续处理请求 if err != nil { log.Errorf("redis call failed: %v", err) return types.ActionContinue } // 暂停处理当前请求头,等待 Redis 脚本调用完成 return types.HeaderStopAllIterationAndWatermark}
// findLimitItem 函数用于在给定的配置中查找与特定消费者匹配的限流项。如果没有找到具体的匹配项,它将返回一个默认的 LimitItem 结构。func findLimitItem(config LimitConfig, key string) LimitItem { // 遍历配置中的所有限流项 for _, limitItem := range config.Limits { // 检查当前限流项的消费者字段是否与提供的 key 匹配,且消费者不是通配符"*" if limitItem.Consumer == key && limitItem.Consumer != "*" { // 如果找到匹配的限流项,返回这个限流项 return limitItem } } // 再次遍历配置中的所有限流项,这次是为了查找通配符"*"的消费者 // 通配符"*"表示这个限流项适用于所有消费者 for _, limitItem := range config.Limits { if limitItem.Consumer == "*" { // 如果找到通配符限流项,返回这个限流项 return limitItem } } // 则返回一个空的 LimitItem 结构,表示没有找到任何适用的限流规则 return LimitItem{}}onHttpRequestHeaders 函数的核心逻辑可以概括为以下几个步骤:
- 获取 Tokens:根据配置(config.InHeader 或 config.InQuery),从请求头或查询参数中提取用于限流的 tokens 信息。
- 验证 Tokens:检查提取的 tokens 是否存在且数量合理(不能多于一个),如果不符合要求,返回相应的错误处理。
- 查找限流项:使用提取的 tokens 查找配置中的限流规则(LimitItem),如果没有找到适用的限流规则,则允许请求继续。
- 执行限流逻辑:如果找到限流规则,构建 Redis 脚本需要的键和参数,然后调用 Redis 脚本执行限流算法。
- 处理 Redis 脚本结果:根据 Redis 脚本返回的结果,创建 LimitContext 对象并根据算法结果决定是否允许请求继续:
- 如果请求被拒绝(context.Allowed <= 0),执行限流逻辑并通知客户端。
- 如果请求被允许,将 LimitContext 对象存储在 HttpContext 中,供后续处理使用。
4 测试和验证
- 正常流量
curl -X POST -v http://127.0.0.1:10000/hello \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer credential1' \ -H 'Content-type: application/json' \ -H 'host:foo.com' \ -d '{"username":["unamexxxx"],"password":["pswdxxxx"]}'
* Trying 127.0.0.1:10000...* Connected to 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1) port 10000 (#0)> POST /hello HTTP/1.1> Host:foo.com> User-Agent: curl/8.1.2> Accept: */*> Authorization: Bearer credential1> Content-type: application/json> Content-Length: 50>< HTTP/1.1 200 OK< content-type: application/json< x-content-type-options: nosniff< date: Tue, 20 Aug 2024 08:55:13 GMT< content-length: 692< req-cost-time: 42< req-arrive-time: 1724144113842< resp-start-time: 1724144113885< x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 8< x-ratelimit-limit: 4< x-ratelimit-remaining: 3< server: envoy<{ "path": "/hello", "host": "foo.com", "method": "POST", "proto": "HTTP/1.1", "headers": { "Accept": [ "*/*" ], "Authorization": [ "Bearer credential1" ], "Content-Length": [ "50" ], "Content-Type": [ "application/json" ], "Original-Host": [ "foo.com" ], "Req-Start-Time": [ "1724144113842" ], "User-Agent": [ "curl/8.1.2" ], "X-Envoy-Expected-Rq-Timeout-Ms": [ "15000" ], "X-Forwarded-Proto": [ "https" ], "X-Request-Id": [ "b40e9ebb-f36c-4e22-b8fc-2559c9495f43" ] }, "namespace": "", "ingress": "", "service": "", "pod": "", "body": { "password": [ "pswdxxxx" ], "username": [ "unamexxxx" ] }可以看到请求被允许,并且返回了相应的响应。
< x-ratelimit-limit: 4< x-ratelimit-remaining: 3- 触发流控
for i in $(seq 1 10); do curl -X POST -v http://127.0.0.1:10000/hello \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer credential1' \ -H 'Content-type: application/json' \ -H 'host:foo.com' \ -d '{"username":["unamexxxx"],"password":["pswdxxxx"]}'done
> POST /hello HTTP/1.1> Host:foo.com> User-Agent: curl/8.1.2> Accept: */*> Authorization: Bearer credential1> Content-type: application/json> Content-Length: 50>< HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests< x-ratelimit-limit: 4< x-ratelimit-remaining: 0< x-ratelimit-reset: 4< content-length: 17< content-type: text/plain< date: Tue, 20 Aug 2024 08:56:57 GMT< server: envoy<* Connection #0 to host 127.0.0.1 left intactToo Many Requests%参考
- [1] 限流算法选择